New Threat in the Middle East
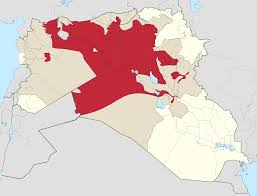
Although turmoil has been consistent in the Middle East, a new kind of threat to humanity emerges to instill fear in the people living in a large part of the Middle East, including Syria and Iraq: The Islamic State of Levant (ISIL). The region is also known by the names The Islamic State of Syria (ISIS), or the Islamic State. The Islamic State has challenged the West with the beheadings of two American journalists and a British aid worker. The US and UN have taken action against the oppressive state and countries all over the world have joined in the effort.
Some background on the state includes its origin in 1999. The group served as a forerunner of the more well-known Al-Qaeda. The radical group of Sunni extremist’s main goal was and is to unite the Muslim world under a single supreme leader who is believed to succeed Mohammed. The group adheres to extreme Sunni ideology and Jihadism, the use of arms for religious duty.
The Islamic State, or ISIS, was “cast off by al-Qaida because” it was “considered too extreme,” said NBC’s David Gregory.
The ISIS followers believe in the need of a Caliphate, defined as the political-religious state comprising the Muslim community and the lands and peoples under its dominion in the centuries following the death (632 ce) of the Prophet Muhammad. ISIS has stated, “The legality of all emirates, groups, states and organizations becomes null by the expansion of the khilafah’s [caliphate’s] authority and arrival of its troops to their areas.”
ISIS members believe that their caliphate is the only legitimate one and even seek to eliminate fellow Sunni groups such as Hamas.
“Violence has bled over the borders of the Syrian Arab republic, with extremism fuelling the conflict’s heightened brutality,” said a UN report released in Geneva.
The UN has accused the ISIS state of serious crimes against humanity such as amputations, public executions, whippings, and crucifixion. The group is also notorious for the murder and oppression of civilians, especially children and women.
“In areas of Syria under ISIS control, particularly in the north and northeast of the country, Fridays are regularly marked by executions, amputations and lashings in public squares,” the same UN report said.
President Obama addressed the nation with his strategy of continued airstrikes to eliminate weapons and IS fighters, deploying American service members to assess and train local forces, and support the National Guard Units to create independence from the IS. He also made it clear that IS is not “Islamic” and is “certainly not a state.” President Obama acknowledged the risks involved and promised that the war would be different from Iraq.
“We will degrade, and ultimately destroy, ISIL through a comprehensive and sustained counter-terrorism strategy” President Obama offered in his speech on the terror threat.
The President continues, “That’s why we must remain vigilant as threats emerge. At this moment, the greatest threats come from the Middle East and North Africa, where radical groups exploit grievances for their own gain.”
FSA Connection Questions
1. In the article, what is the main conflict?
2. In this piece, what does Jihadism mean?
3. What is President Obama’s strategy against ISIL?
4. What is the connotation of the word ‘exploit’ in this piece?
5. Select one sentence that best summarizes the work.

Kevin “K.Chow” Chow is currently a senior at Freedom High School. He was born in Auckland, New Zealand and his family relocated to Australia and Tampa....










